Problem-solving and decision making

Problem solving
The Concise Oxford Dictionary (1995) defines a problem as “A doubtful or difficult matter requiring a solution” and “Something hard to understand or accomplish or deal with” (Problem Solving, n.d.). Throughout our lives we are about to face numerous problems, either essential or less significant, in all the areas of our activity, such as personal, professional, financial or social. When we need to solve a problem, there are some steps we can follow, in order to facilitate this process and deal with the problem (What Is Problem Solving? Steps, Process & Techniques | ASQ, n.d.).
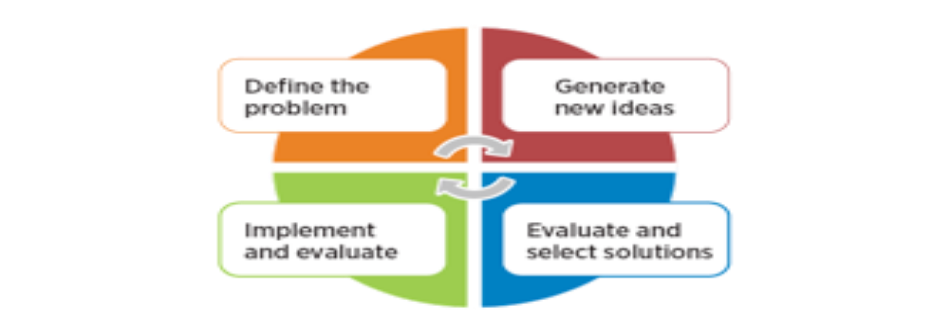
STEP 1
Define the problem: The definition of the problem is of vital importance, in order to achieve a successful solution. Find out the nature of the problem and possible underlying causes and state the problem specifically. Avoid attempting to solve the problem without sufficient data.
STEP 2
Generate new ideas: In this stage generation of alternative solutions will start. Multiple alternatives will enhance the selection of the ideal solution. So, start brainstorming and encourage others to do so, in order to gather new ideas and points of view. But be careful! Avoid in this stage to select a solution and don’t make a decision in a hurry, before listening to all the proposals.
STEP 3
Evaluate and select a solution: In this part you have to decide which of the suggested solutions you will choose. In order to evaluate them and make up your mind, you need to take into consideration:
- Whether the particular alternative will solve the problem without generating more problems.
- If all included members accept this solution.
- If the implementation of the solution is feasible.
- If the solution is complied with the organizational constraints regarding a working environment.
STEP 4
Implement and evaluate: When you make the decision, you must plan your next moves and proceed with the implementation of the chosen course of action. After the implementation, there should be a follow up on the outcomes and an assessment on whether the solution was successful or not. Receive feedback from people affected by the solution and keep monitoring the progress.
Decision making
Decision making is the process of making choices by gathering information and evaluating alternative solutions (University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, 2020). This process consists of seven steps to help you organize relevant information and make a final decision.
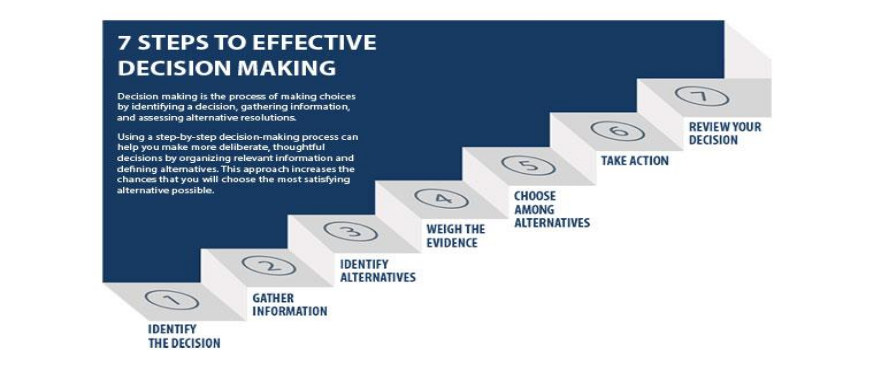
STEP 1
Identify the decision: When you understand there is a need to make a decision, try to define the nature of the decision before you move on to the following steps.
STEP 2
Gather relevant information: It is really important to collect information related to your decision. Think about what kind of information is needed and how to get it. This requires both internal (you will seek information through a self – assessment process) and external search (via Internet, books or other people).
STEP 3
Identify the alternatives: In this stage, by seeking information, you will come across several alternatives. You have to collect the most desirable and feasible alternatives.
STEP 4
Weigh the evidence: After collecting the information needed and being aware of all the possible alternatives, you have to contemplate which alternative meets better the needs of your decision. Imagine the implementation of a certain alternative and think whether it is suitable. You can also prioritize the alternatives according to your own value system.
STEP 5
Choose among alternatives: In this stage you need to make a choice. You might select a combination of the proposed alternatives.
STEP 6
Take action: You are ready to take action in order to implement the alternative you chose in step 5.
STEP 7
Review your decision & its consequences: Think about the outcomes of your choice and evaluate them. In case the decision didn’t meet the needs you identified in step 1, you may have to repeat some steps and gather further and more detailed information.

